The PV diagram models the relationship between pressure (P) and volume (V) for an ideal gas. An ideal gas is one that never condenses regardless of the various changes its state variables (pressure, volume, temperature) undergo. [1] In addition, the processes plotted on PV diagrams only work for a closed system (in this case the ideal gas), so.. p-v-Diagramm des Diesel-Prozesses Vergleich von Adiabate und Isotherme für ein ideales Gas. Das p-v-Diagramm ist eine spezielle Form eines Zustandsraums eines Gases (bzw. Fluids), bei der der Druck p eines Systems gegen das spezifische Volumen v aufgetragen wird. Ein bestimmtes Gas ist somit immer durch einen Punkt auf dem p-v-Diagramm beschrieben. Verwendet man anstatt des spezifischen.

PVDiagramme und ViertaktOttomotoren einfach erklärt YouTube

PV DIAGRAM OF IDEAL GAS STANDARD LIMITED PRESSURE CYCLE Download Scientific Diagram

11 Ideal and NonIdeal Gases The Live Textbook of Physical Chemistry 1

Real Gases Introduction to Chemistry

gas laws Pressure Vs Volume plot for real and ideal gasses Chemistry Stack Exchange
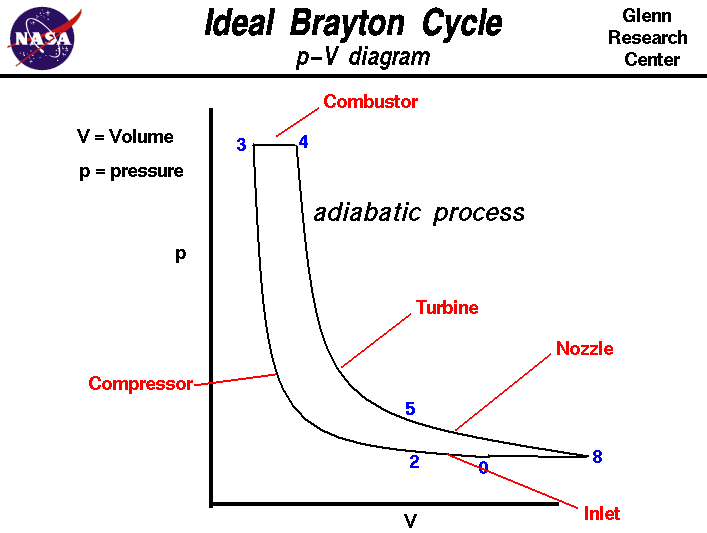
Turbine Engine Thermodynamic Cycle Brayton Cycle
Consider P=V diagram for an ideal gas shown in Fig.… SolvedLib

Phase Changes · Physics

Isobutane Phase Diagram

pV diagram comparing ideal airstandard cycles Download Scientific Diagram
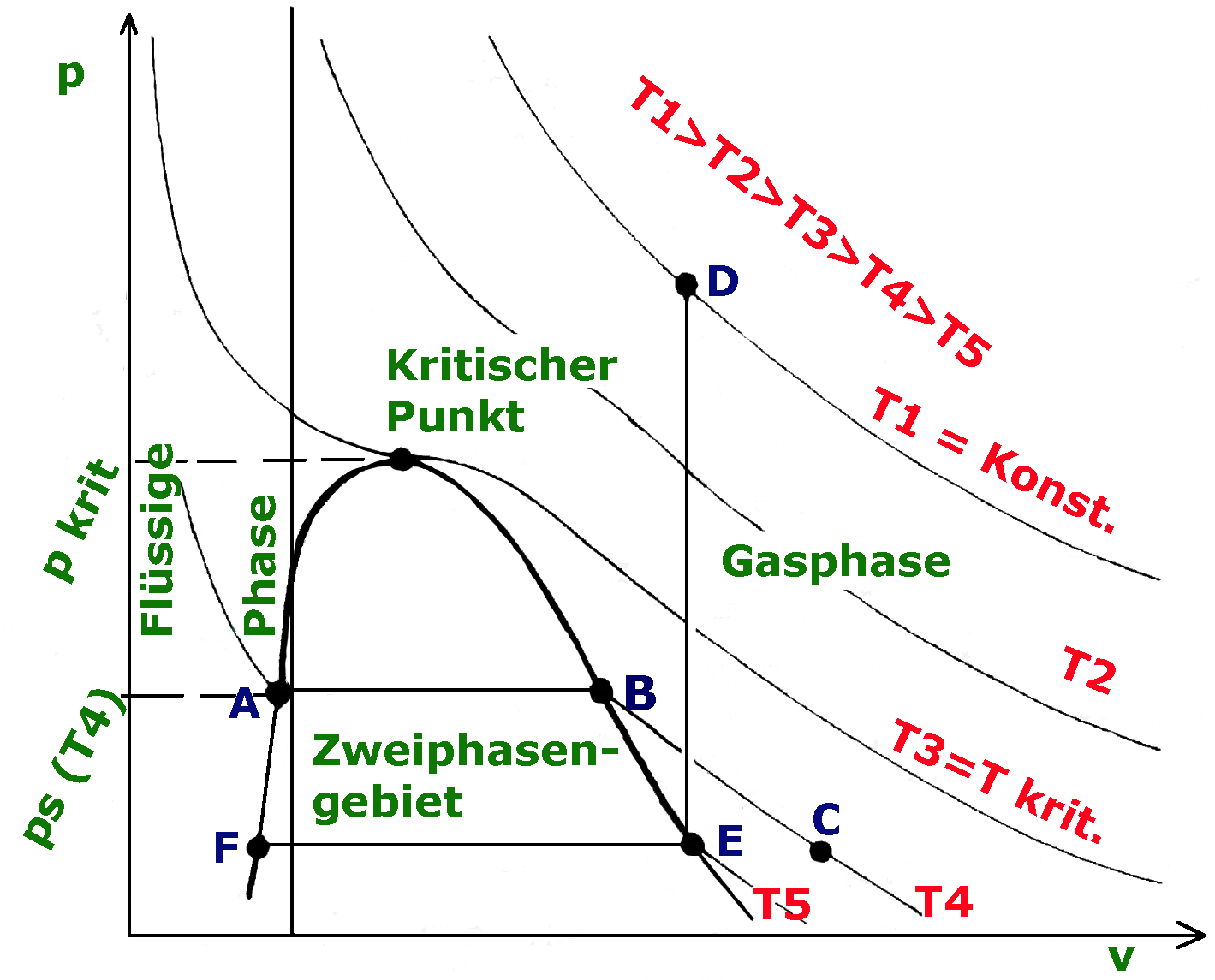
Tiefkalte flüssige Gase p V T Diagramm
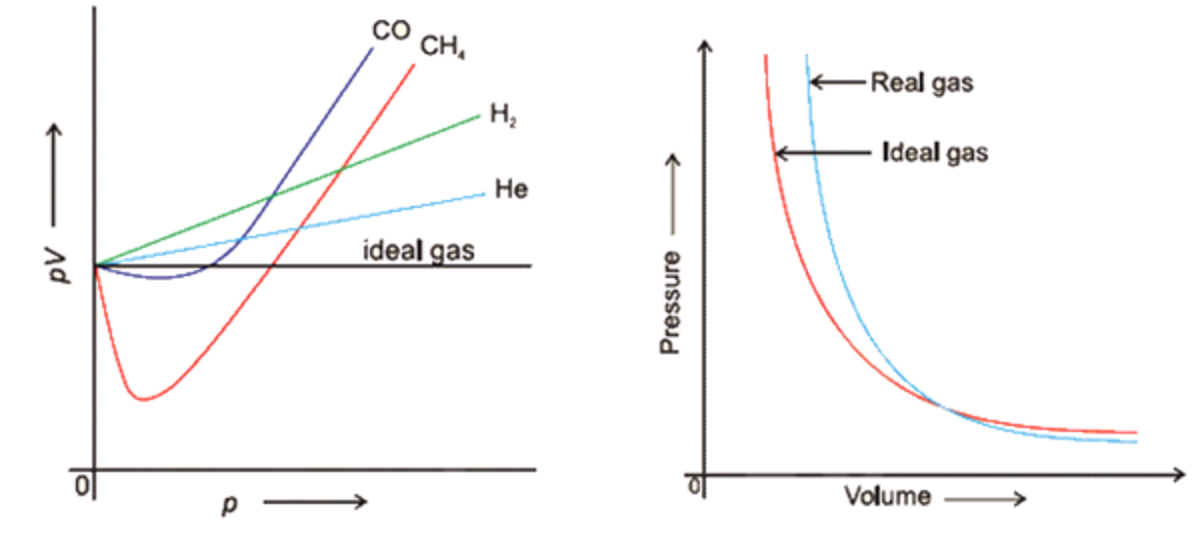
Real Gases Chemistry, Class 11, States of Matter

P − V diagram of Van der Waals fluid. The temperature of isotherms... Download Scientific Diagram

11 Ideal and NonIdeal Gases The Live Textbook of Physical Chemistry 1

Erklärung der Verflüssigung von Gasen (VanderWaalsGleichung) tecscience

11.4.3 PV Diagram xmPhysics

A pv diagram of carbon dioxide (CO2). Gas densities of interest are... Download Scientific
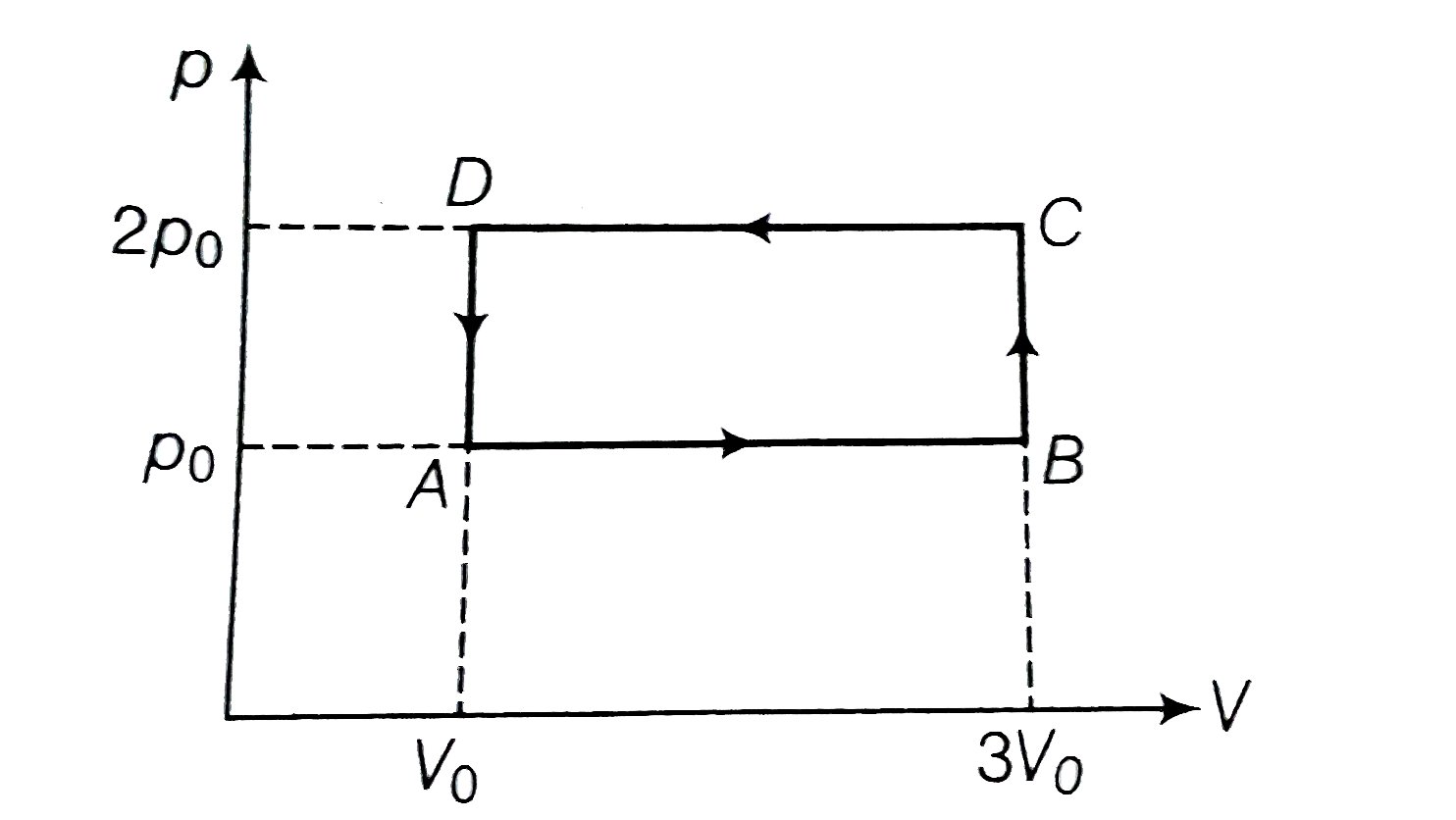
PV diagram of an ideal gas is shown in the figure. Work done by the gas in the process ABCD is

One mole of monoatomic ideal gas undergoes the thermodynamic process a → b shown in P V

thermodynamics Please explain the shape of the isotherms in this PV phase diagram Physics
Diese Zustandsgleichung wird „Van-der-Waals-Zustandsgleichung" genannt. Sie ist eine Gleichung 3. Grades der Variablen V, so dass sich beim Auftragen von p gegen V in p-V-Diagramm (statt Hyperbeln im Fall des idealen Gases) Kurven 3. Ordnung ergeben, welche Minima, Maxima und Wendepunkte erhalten. Falls T konstant ist, sind diese Kurven.. Für ideale Gase K15.1 kennt man die Zustandsgleichung und diese genügt, um die Gleichungen der verschiedenartigen Zustandsänderungen (isotherm, adiabatisch usw.) ohne neue Experimente herzuleiten. Für reale Gase gibt es keine allgemeine Zustandsgleichung und daher muss man für die genannten Zustandsänderungen neue Beobachtungen zu Hilfe.